An association between clinical and biochemical criteria of metabolic syndrome and alanine aminotransferase levels in a sample of children with overweight and obesity, in Lima-Peru: A single-center cross-sectional study, 2015-2019
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.58597/rpe.v4i1.92Keywords:
Alanine Aminotransferase, Overweight, Pediatric Obesity, Metabolic SyndromeAbstract
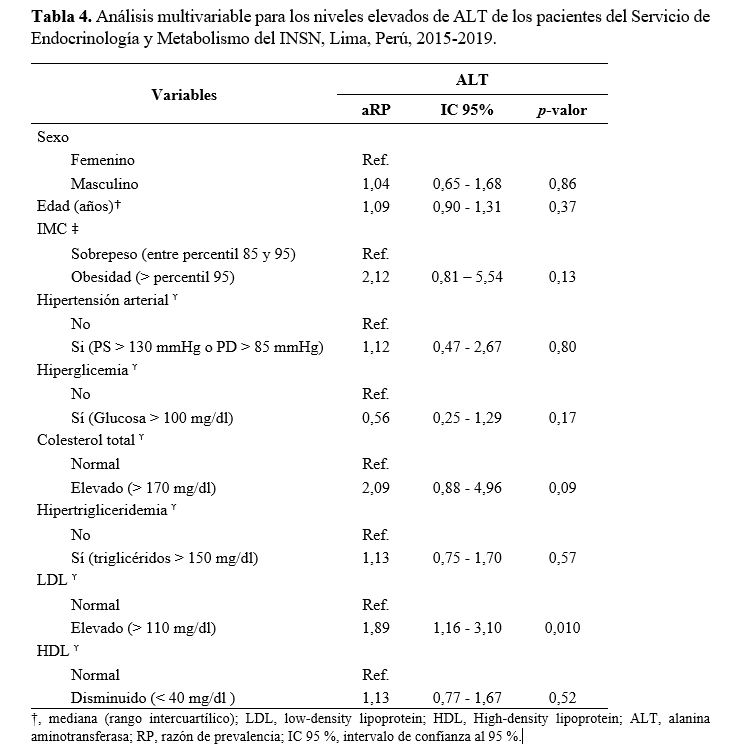
Objective: To determine the association between clinical/biochemical criteria of metabolic syndrome and alanine aminotransferase (alt) levels in patients attended in the Endocrinology and Metabolism service of the Instituto Nacional de Salud del Niño between January 2015 and December 2019. Materials and methods: An analytical, retrospective cross-sectional study based on medical records of patients between 10 and 18 years of age with overweight or obesity. Bivariate and multivariate statistics were used to determine the associations between overweight groups and ALT levels. Results: A 39.3% of the sample presented high ALT levels. However, ALT levels were higher in the group of patients with obesity (42.4%). Only patients with obesity and high ALT levels showed increased total cholesterol and LDL (p < 0.05). According to the multivariate model, high LDL would function as a predictor of high ALT in overweight pubescent and adolescent patients (PR = 1.89; 95 % CI: 1.16 - 3.10). Conclusions: High LDL was associated with high ALT levels, which could be an indicator of cardiovascular disease, probably due to liver involvement. Further longitudinal studies are still required to establish causal associations.
Downloads
References
World Health Organization. UNICEF / WHO / The World Bank Group joint child malnutrition estimates: key findings of the 2023 edition. WHO. 2023 [ Citado 27 de febrero de 2025]. Disponible en: https://www.who.int/data/gho/data/themes/topics/joint-child-malnutrition-estimates-unicef-who-wb
Instituto Nacional de Salud. Estado Nutricional en Niños de 6 a 13 años: 2017-2018. Informe técnico de la Vigilancia Alimentaria y Nutricional por etapas de vida: Niños 2017-2018 [Internet]. INS; 2023 [Citado el 06 de marzo del 2025]. Disponible en: https://www.gob.pe/institucion/ins/informes-publicaciones/4202391-informe-tecnico-estado-nutricional-en-ninos-de-6-a-13-anos-vianev-2017-2018
Morandi A, Maffeis C. Predictors of metabolic risk in childhood obesity. Horm Res Paediatr. 2014;82(1):3-11. doi: 10.1159/000362237.
Selvakumar PKC, Kabbany MN, Nobili V, Alkhouri N. Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Children: Hepatic and Extrahepatic Complications. Pediatr Clin North Am. 2017;64(3):659-675. doi: 10.1016/j.pcl.2017.01.008.
Miele L, Targher G. Understanding the association between developing a fatty liver and subsequent cardio-metabolic complications. Expert Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2015;9(10):1243-5. doi: 10.1586/17474124.2015.1074860.
Patton H, Sirlin C, Behling C, Middleton M, Schwimmer JB, Lavine JE. Pediatric nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: a critical appraisal of current data and implications for future research. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2006;43(4):413-27. doi: 10.1097/01.mpg.0000239995.58388.56.
Sarmiento F, Botero V, D´Agostino D, Delgado L, Dewaele M, Guzmán P, et al. Enfermedad de hígado graso no alcohólico (EHGNA): revisión y puesta al día. Grupo de trabajo de la Sociedad Latinoamericana de Gastroenterología Hepatología y Nutrición Pediátrica (SLAGHNP). Acta Gastroenterol Latinoam. 2016;46(3):246-264. Disponible em: https://actagastro.org/enfermedad-de-higado-graso-no-alcoholico-ehgna-revision-y-puesta-al-dia-grupo-de-trabajo-de-la-sociedad-latinoamericana-de-gastroenterologia-hepatologia-y-nutricion-pediatrica-slaghnp/
Vos MB, Abrams SH, Barlow SE, Caprio S, Daniels SR, Kohli R, Mouzaki M, Sathya P, Schwimmer JB, Sundaram SS, Xanthakos SA. NASPGHAN Clinical Practice Guideline for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Children: Recommendations from the Expert Committee on NAFLD (ECON) and the North American Society of Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition (NASPGHAN). J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2017;64(2):319-334. doi: 10.1097/MPG.0000000000001482.
van Vliet M, von Rosenstiel IA, Schindhelm RK, Brandjes DP, Beijnen JH, Diamant M. The association of elevated alanine aminotransferase and the metabolic syndrome in an overweight and obese pediatric population of multi-ethnic origin. Eur J Pediatr. 2009;168(5):585-91. doi: 10.1007/s00431-008-0802-2.
Cabrera Y, Martínez M, Cabello A, Pereyra S, Villafuerte S, Cabello E. Alanina aminotransferasa como marcador en el diagnóstico de Síndrome Metabólico y riesgo cardiovascular en niños con obesidad. Acta Med Per. 2019;36(4):253-8. Disponible en: http://www.scielo.org.pe/scielo.php?pid=S1728-59172019000400002&script=sci_abstract
Samani SG, Kelishadi R, Adibi A, Noori H, Moeini M. Association of serum alanine aminotransferase levels with cardiometabolic risk factors in normal-weight and overweight children. Iran J Pediatr. 2011;21(3):287-93. Disponible en: https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC3446178/
Instituto Nacional de Salud del Niño. Análisis situacional de los servicios de salud en el INSN año 2019 (ASIS). Perú: INSN. 2019[Internet]. Lima: Gob.pe, 2019[Citado el 07 de marzo del 2025]. Disponible en: https://www.gob.pe/institucion/insn/informes-publicaciones/4897034-analisis-de-situacion-de-salud-insn-2019
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Child and Teen BMI Categories[Internet]. United States: CDC. 2024[Citado el 07 de marzo del 2025]. Disponible en: https://www.cdc.gov/bmi/child-teen-calculator/bmi-categories.html
Equator Network. The Strengthening the Reporting of Observational Studies in Epidemiology (STROBE)Statement: guidelines for reporting observational studies[Internet]. Oxford: Equator Network; 2023[Citado el 07 de marzo del 2025]. Disponible en: https://www.equator-network.org/reporting-guidelines/strobe/
Fraser A, Longnecker MP, Lawlor DA. Prevalence of elevated alanine aminotransferase among US adolescents and associated factors: NHANES 1999-2004. Gastroenterology. 2007;133(6):1814-20. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2007.08.077.
Pickering TG, Hall JE, Appel LJ, Falkner BE, Graves J, Hill MN, et al. Recommendations for blood pressure measurement in humans and experimental animals: part 1: blood pressure measurement in humans: a statement for professionals from the Subcommittee of Professional and Public Education of the American Heart Association Council on High Blood Pressure Research. Circulation. 2005;111(5):697-716. doi: 10.1161/01.CIR.0000154900.76284.F6..
Zimmet P, Alberti KG, Kaufman F, Tajima N, Silink M, Arslanian S, et al. The metabolic syndrome in children and adolescents - an IDF consensus report. Pediatr Diabetes. 2007;8(5):299-306. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-5448.2007.00271.x.
Expert Panel on Integrated Guidelines for Cardiovascular Health and Risk Reduction in Children and Adolescents; National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute. Expert panel on integrated guidelines for cardiovascular health and risk reduction in children and adolescents: summary report. Pediatrics. 2011;128 Suppl 5(Suppl 5):S213-56. doi: 10.1542/peds.2009-2107C.
IBM Corp. IBM SPSS Statistics [software] versión 25.0 para Windows. Armonk, NY: IBM Corp., 2022. Disponible en: https://www.ibm.com/mx-es/products/spss-statistics
Burgert TS, Taksali SE, Dziura J, Goodman TR, Yeckel CW, Papademetris X, Constable RT, Weiss R, Tamborlane WV, Savoye M, Seyal AA, Caprio S. Alanine aminotransferase levels and fatty liver in childhood obesity: associations with insulin resistance, adiponectin, and visceral fat. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2006;91(11):4287-94. doi: 10.1210/jc.2006-1010.
Hartman C, Rennert HS, Rennert G, Elenberg Y, Zuckerman E. Prevalence of elevated liver enzymes and comorbidities in children and adolescents with overweight and obesity. Acta Paediatr. 2021;110(3):985-992. doi: 10.1111/apa.15469.
García-López N, Jiménez-Álvarez A, Murillo-Zamora E. Detección de hígado graso no alcohólico en niños con sobrepeso y obesidad. Rev Med Inst Mex Seguro Soc. 2021;59(6):465-72. Disponible en: https://www.redalyc.org/journal/4577/457769655006/html/
Putri RR, Casswall T, Hagman E. Prevalence of increased transaminases and its association with sex, age, and metabolic parameters in children and adolescents with obesity - a nationwide cross-sectional cohort study. BMC Pediatr. 2021;21(1):271. doi: 10.1186/s12887-021-02747-4.
Wei C, Ford A, Hunt L, Crowne EC, Shield JP. Abnormal liver function in children with metabolic syndrome from a UK-based obesity clinic. Arch Dis Child. 2011;96(11):1003-7. doi: 10.1136/adc.2010.190975.
Thiagarajan S, Shrinuvasan S, Arun Babu T. Screening for non-alcoholic fatty liver disease among obese and overweight children: Prevalence and predictors. Indian J Gastroenterol. 2022;41(1):63-68. doi: 10.1007/s12664-021-01198-0.
Jin B, Wu Z, Wang S, Yu Z, Ullah R, Liang X, et al. Gender differences in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in obese children and adolescents: a large cross-sectional study. Hepatol Int. 2024;18(1):179-187. doi: 10.1007/s12072-023-10596-9.
Zhou L, Zhang L, Zhang L, Yi W, Yu X, Mei H, et al. Analysis of risk factors for non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in hospitalized children with obesity before the late puberty stage. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023;14:1224816. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1224816.
Di Sessa A, Grandone A, Marzuillo P, Umano GR, Cirillo G, Miraglia Del Giudice E. Early menarche is associated with insulin-resistance and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in adolescents with obesity. J Pediatr Endocrinol Metab. 2021;34(5):607-612. doi: 10.1515/jpem-2020-0684.
Flores-Calderón J, Gómez-Díaz RA, Rodríguez-Gómez G, Morán-Villota S. Frequency of increased aminotransferases levels and associated metabolic abnormalities in obese and overweight children of an elementary school in Mexico City. Ann Hepatol. 2005;4(4):279-83. Disponible en: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16432495/
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Rosa María Tucto-Manchego, Carlos Manuel Del Águila-Villar, Luis Rómulo Lu-de Lama, Oswaldo Núñez-Almache, Eliana Manuela Chávez-Tejada, Oscar Antonio Espinoza-Robles, Paola Marianella Pinto-Ibárcena, Martha Rosario Calagua-Quispe, Miguel Ángel De los Santos-La Torre, Pamela Miluska Azabache-Tafur

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.