Prevalence of metabolic syndrome in obese patients treated at a specialized pediatric institute, Peru, 2018-2022
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.58597/rpe.v3i4.82Keywords:
Metabolic Syndrome, Adolescent, Diagnosis, Dyslipidemias, ObesityAbstract
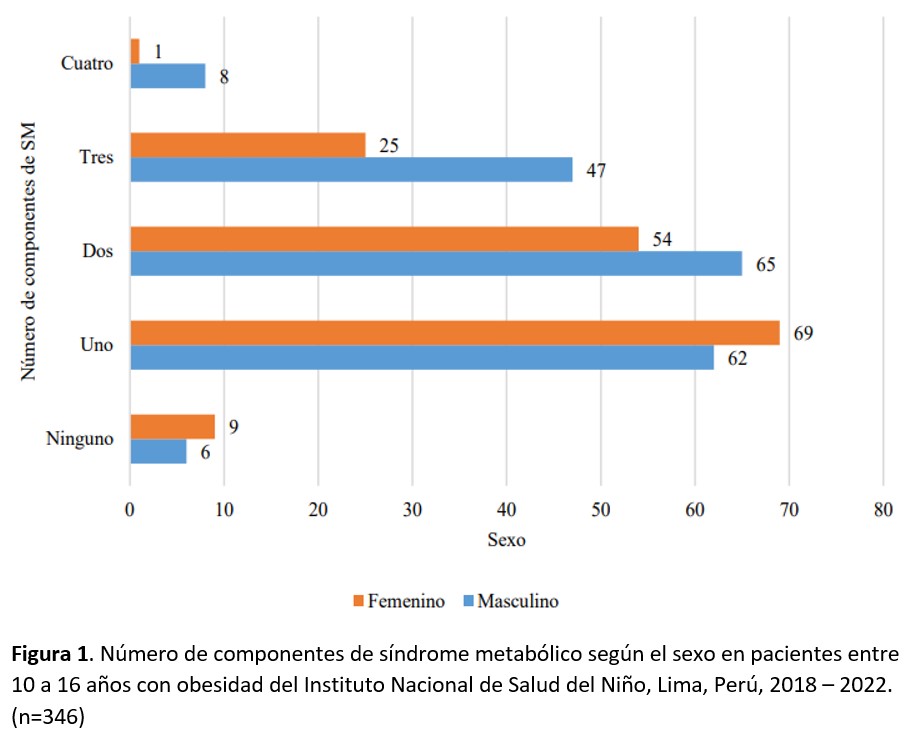
Objective: To determine the prevalence of metabolic syndrome (MS) and its components in patients with obesity aged 10 to 16 years at a specialized pediatric institute in Peru from 2018 to 2022. Materials and methods: This is a descriptive, retrospective, and cross-sectional study. The population consisted of 3,462 medical records of patients with obesity, from which 346 were selected based on a sample size calculation. The variables were defined according to the International Diabetes Federation criteria for MS. For the bivariate analysis, the chi-square test was used for categorical variables, and the Mann-Whitney U test for the numerical variable, considering a p-value < 0.05 as significant, using Stata v.17 software. Results: Of the 346 patients with obesity, 55.2% were male with an average age of 11.8 years (SD: ±1.7). A total of 23.4% met the criteria for MS, with a higher prevalence observed in males (p = 0.009). Among those with three and four components of MS, there were 72 and 9 cases, respectively. The most frequent components were abdominal obesity > 90th percentile, triglycerides >150 mg/dL, and HDL <40 mg/dL, with statistically significant differences (p < 0.001). Conclusion: The prevalence of MS in this population shows an increasing trend compared to previous Peruvian studies, with a predominance of abdominal obesity and dyslipidemia components (low HDL and hypertriglyceridemia), while hyperglycemia and high blood pressure were less common. This finding highlights the need for early interventions to prevent long-term metabolic complications.
Downloads
References
Jebeile H, Kelly AS, O'Malley G, Baur LA. Obesity in children and adolescents: epidemiology, causes, assessment, and management. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2022;10(5):351-365. doi: 10.1016/S2213-8587(22)00047-X.
Simmonds M, Llewellyn A, Owen CG, Woolacott N. Simple tests for the diagnosis of childhood obesity: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Obes Rev. 2016;17(12):1301-1315. doi: 10.1111/obr.12462.
World Obesity Federation Global obesity observatory. 2021. https://data.worldobesity.org/maps/?area=trends
NCD Risk Factor Collaboration (NCD-RisC). Worldwide trends in body-mass index, underweight, overweight, and obesity from 1975 to 2016: a pooled analysis of 2416 population-based measurement studies in 128•9 million children, adolescents, and adults. Lancet. 2017; 390(10113):2627-2642. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(17)32129-3.
Obesity and Overweight. World Health Organization (WHO). Available from: [Internet] https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/obesity-and-overweight
Pulungan AB, Puteri HA, Ratnasari AF, Hoey H, Utari A, Darendeliler F, et al. Childhood Obesity as a Global Problem: a Cross-sectional Survey on Global Awareness and National Program Implementation. J Clin Res Pediatr Endocrinol. 2024;16(1):31-40. doi: 10.4274/jcrpe.galenos.2023.2023-7-5.
Ferentinou E, Koutelekos I, Pappa D, Manthou P, Dafogianni C. The Impact of the COVID-19 Pandemic on Childhood Obesity: A Review. Cureus. 2023;15(9):e45470. doi: 10.7759/cureus.45470.
Gepstein V, Weiss R. Obesity as the Main Risk Factor for Metabolic Syndrome in Children. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2019;10:568. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2019.00568.
Ciężki S, Odyjewska E, Bossowski A, Głowińska-Olszewska B. Not Only Metabolic Complications of Childhood Obesity. Nutrients. 2024;16(4):539. doi: 10.3390/nu16040539.
Halpern A, Mancini MC, Magalhães ME, Fisberg M, Radominski R, Bertolami MC, et al. Metabolic syndrome, dyslipidemia, hypertension and type 2 diabetes in youth: from diagnosis to treatment. Diabetol Metab Syndr. 2010;2:55. doi: 10.1186/1758-5996-2-55.
Ford ES, Li C. Defining the metabolic syndrome in children and adolescents: will the real definition please stand up? J Pediatr. 2008;152(2):160-4. doi: 10.1016/j.jpeds.2007.07.056.
Zimmet P, Alberti KG, Kaufman F, Tajima N, Silink M, Arslanian S; IDF Consensus Group. The metabolic syndrome in children and adolescents - an IDF consensus report. Pediatr Diabetes. 2007;8(5):299-306. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-5448.2007.00271.x.
Kassi E, Pervanidou P, Kaltsas G, Chrousos G. Metabolic syndrome: definitions and controversies. BMC Med. 2011;9:48. doi: 10.1186/1741-7015-9-48.
Orsini F, D'Ambrosio F, Scardigno A, Ricciardi R, Calabrò GE. Epidemiological Impact of Metabolic Syndrome in Overweight and Obese European Children and Adolescents: A Systematic Literature Review. Nutrients. 2023;15(18):3895. doi: 10.3390/nu15183895.
Bitew ZW, Alemu A, Ayele EG, Tenaw Z, Alebel A, Worku T. Metabolic syndrome among children and adolescents in low and middle income countries: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Diabetol Metab Syndr. 2020;12:93. doi: 10.1186/s13098-020-00601-8.
Romaní-Romaní F, Pachacama Ramirez LF, Pichihua Grandez JD, Guevara Rodríguez DM, Cornejo Luyo V, Sheen Vargas CE, et al. Concordancia entre cinco criterios de síndrome metabólico en adolescentes de una zona altoandina del Perú. Rev Peru Med Exp Salud Pública. 2023;40(2):150-60. doi: 10.17843/ rpmesp.2023.402.12546.
Pajuelo J, Bernui I, Nolberto V, Peña A, Zevillanos L. Síndrome metabólico en adolescentes con sobrepeso y obesidad. An Fac Med Lima. 2007;68(2):143-9. Disponible en: http://www.scielo.org.pe/scielo.php?pid=S1025-55832007000200006&script=sci_arttext
Szabelska-Zakrzewska K, Durko A, Socha-Banasiak A, Majewska M, Kolejwa M, Kazanek-Zasada J, et al. Metabolic syndrome in overweight or obese children and adolescents based on own material. Dev Period Med. 2018;22(4):351-357. doi: 10.34763/devperiodmed.20182204.351357.
Cua SC. Prevalence of Metabolic Syndrome in Overweight and Obese Filipino Adolescents Based on the IDF Definition. J ASEAN Fed Endocr Soc. 2014;27(1):82. Avaliable in: https://asean-endocrinejournal.org/index.php/JAFES/article/view/18/32
Smetanina N, Valickas R, Vitkauskiene A, Albertsson-Wikland K, Verkauskienė R. Prevalence of Metabolic Syndrome and Impaired Glucose Metabolism among 10- to 17-Year-Old Overweight and Obese Lithuanian Children and Adolescents. Obes Facts. 2021;14(3):271-282. doi: 10.1159/000514720.
Mahbuba S, Mohsin F, Rahat F, Nahar J, Begum T, Nahar N. Descriptive epidemiology of metabolic syndrome among obese adolescent population. Diabetes Metab Syndr. 2018;12(3):369-374. doi: 10.1016/j.dsx.2017.12.026.
Tavares Giannini D, Caetano Kuschnir MC, Szklo M. Metabolic syndrome in overweight and obese adolescents: a comparison of two different diagnostic criteria. Ann Nutr Metab. 2014; 64(1):71-9. doi: 10.1159/000362568.
Sangun Ö, Dündar B, Köşker M, Pirgon Ö, Dündar N. Prevalence of metabolic syndrome in obese children and adolescents using three different criteria and evaluation of risk factors. J Clin Res Pediatr Endocrinol. 2011;3(2):70-6. doi: 10.4274/jcrpe.v3i2.15.
Wan Mahmud Sabri WMN, Mohamed RZ, Yaacob NM, Hussain S. Prevalence of Metabolic Syndrome and its Associated Risk Factors in Pediatric Obesity. J ASEAN Fed Endocr Soc. 2022;37(1):24-30. doi: 10.15605/jafes.037.01.05.
Alosaimi N, Sherar LB, Griffiths P, Pearson N. Clustering of diet, physical activity and sedentary behaviour and related physical and mental health outcomes: a systematic review. BMC Public Health. 2023;23(1):1572. doi: 10.1186/s12889-023-16372-6.
Ferrari GLM, Kovalskys I, Fisberg M, Gomez G, Rigotti A, Sanabria LYC; ELANS Study Group. Anthropometry, dietary intake, physical activity and sitting time patterns in adolescents aged 15-17 years: an international comparison in eight Latin American countries. BMC Pediatr. 2020;20(1):24. doi: 10.1186/s12887-020-1920-x.
Cornejo-Monthedoro A, Negreiros-Sánchez I, Del Águila C, Ysla-Marquillo M, Mayta-Tristán P. Association between dietary glycemic load and metabolic syndrome in obese children and adolescents. Arch Argent Pediatr. 2017;115(4):323-330. doi: 10.5546/aap.2017.eng.323.
Bernabe-Ortiz A, Mendoza-Quispe D, Jimenez MM, Ugaz ME, Rojas-Dávila CE. Quantifying the childhood and adolescent overnutrition attributable to specific risk factors: The Young Lives Study in Peru. Pediatr Obes. 2023;18(4):e13002. doi: 10.1111/ijpo.13002.
Pourghazi F, Eslami M, Ehsani A, Ejtahed HS, Qorbani M. Eating habits of children and adolescents during the COVID-19 era: A systematic review. Front Nutr. 2022;9:1004953. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2022.1004953.
Liao Z, Vosberg DE, Pausova Z, Paus T. A Shifting Relationship Between Sex Hormone-Binding Globulin and Total Testosterone Across Puberty in Boys. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2022;107(10):e4187-e4196. doi: 10.1210/clinem/dgac484.
Ramírez Alvarado MM, Sánchez Roitz C. El factor de necrosis tumoral-α, la resistencia a la insulina, el metabolismo de lipoproteínas y la obesidad en humanos. Nutr. Hosp. 2012;27(6): 1751-1757. doi: 10.3305/nh.2012.27.6.6004.
Jakobsen DD, Brader L, Bruun JM. Association between Food, Beverages and Overweight/Obesity in Children and Adolescents-A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Observational Studies. Nutrients. 2023;15(3):764. doi: 10.3390/nu15030764.
Li H, Zhang W, Yan J. Physical activity and sedentary behavior among school-going adolescents in low- and middle-income countries: insights from the global school-based health survey. Peer J. 2024; 12:e17097. doi: 10.7717/peerj.17097.
Pierlot R, Cuevas-Romero E, Rodríguez-Antolín J, Méndez-Hernández P, Martínez-Gómez M. Prevalencia de Síndrome Metabólico en niños y adolescentes de América. TIP. 2017;20(1): 40-49. doi: 10.1016/j.recqb.2016.11.004.
Hampl SE, Hassink SG, Skinner AC, Armstrong SC, Barlow SE, Bolling CF, et al. Clinical Practice Guideline for the Evaluation and Treatment of Children and Adolescents With Obesity. Pediatrics. 2023;151(2):e2022060640. doi: 10.1542/peds.2022-060640. Erratum in: Pediatrics. 2024; 153(1):e2023064612. doi: 10.1542/peds.2023-064612.
García SA, Ninatanta-Ortiz JA, Abanto MV, Pérez KM, Chávez RR, Palacios SE, et al. Intervención educativa basada en estilos de vida para incrementar la proporción de adolescentes libres de componentes del síndrome metabólico en una región altoandina del Perú. Rev Peru Med Exp Salud Pública. 2022;39(1):36-46. doi: 10.17843/rpmesp.2022.391.9986.
Migueles JH, Cadenas-Sanchez C, Lubans DR, Henriksson P, Torres-Lopez LV, Rodriguez-Ayllon M, et al. Effects of an Exercise Program on Cardiometabolic and Mental Health in Children With Overweight or Obesity: A Secondary Analysis of a Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Netw Open. 2023;6(7):e2324839. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.24839. Erratum in: JAMA Netw Open. 2024;7(5):e2419953. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.19953.
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Denisse Colina-Cisneros, Carlos Manuel Del Águila-Villar, Luis Rómulo Lu-De Lama, Oswaldo Núñez-Almache , Eliana Manuela de Jesús Chávez-Tejada, Óscar Espinoza Robles, Paola Marianella Pinto-Ibárcena, Martha Rosario Calagua-Quispe, Miguel Ángel De Los Santos-La Torre, Pamela Miluska Azabache-Tafur

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.