Ambiente educacional y aprendizaje autorregulado de los residentes de pediatría de un hospital especializado durante la pandemia por COVID-19
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.58597/rpe.v2i2.44Keywords:
Internship and Residency, Pediatrics, Learning, Self-directed learning as topic, Educational environmentAbstract
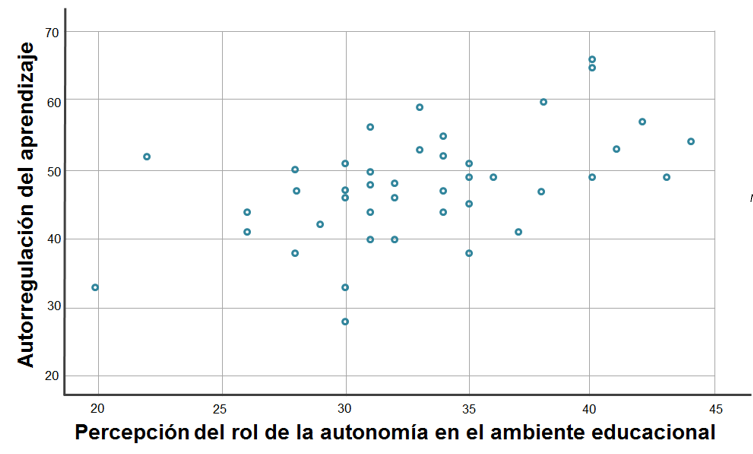
Objective: To connect the perception of the educational environment and self-regulated learning of pediatric residents of Instituto Nacional de Salud del Niño (National Institute of Children’s Health) in Lima, Peru, during COVID-19 pandemics in 2021. Materials and methods: Analytical mixed-approach study. In the quantitative phase, the Post Graduate Hospital Educational Environment Mesure (PHEEM) questionnaire and a self-regulated learning questionnaire were applied in a sample of 60 pediatric residents. In the qualitative phase, in-depth interviews with 12 residents were conducted between May and June 2021. Results: The evaluation produced a predominantly positive perception of the educational environment (80%; p = 0.837) and, in relation to self-regulated learning, there were average scores between 2 and 3. There was a direct correlation between the educational environment and self-regulated learning (r = 0.422; p = 0.001). Communication and resident-patient relationship seem to be important factors for establishing study strategies and objectives. Conclusion: A favorable educational environment is needed for a good self-regulated learning at motivational and cognitive levels. Although COVID-19 pandemics weakened the interaction between people within the hospital environment, it is possible to seek strategies to improve learning. These results cannot be generalized.
Downloads
Downloads
Additional Files
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2023 Jaime Pezo Morales, Andrea Vanessa Bravo Cárdenas, César Augusto Pupuche Senador

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.